Notes for AI Product Management
Notes for AI Product Management
This is the note for course CS-500 AI Product Management (AIPM).
Week 1
In week 1 we mainly learned what is Product Management (PM) and what is AI Product Management (AIPM).
Class Notes
- Attention is required for this course.
- AI is a general-purpose technology.
- Value and needs
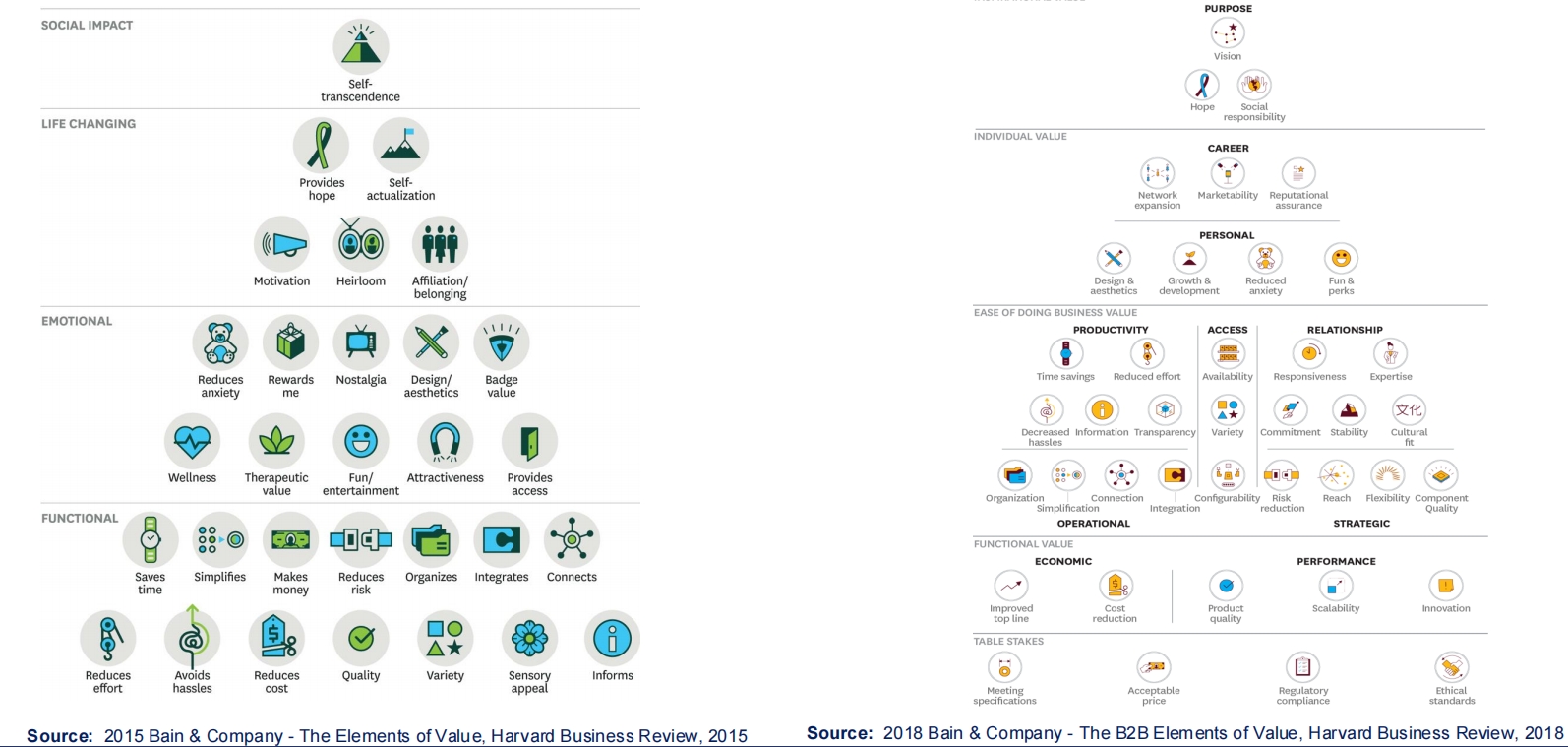
- From product to systems of systems
- Product -> Smart product -> Smart, connected product -> Product System -> System of systems
- Success factors
- Valuable
- Feasible
- Viable
Resources
The nature of product | Marty Cagan, Silicon Valley Product Group
- What is a product manager
- Product manager: Problem -> Solution (Valuable and viable)
- Project manager: Jira, Sprint…
- Issues of big companies
- As company grows, they value more on marketing, finance than product.
- Value creation (discovery) v.s. value capture (optimization)
- User research
- Find reasons why users won’t use your product.
- PM needs to be present at user research tests.
Case Galleries
- Stacksync
- Amazon go
Week 2
In week 2 we discussed some technical issues for AI start-ups, and pitched our project.
Resources
How to Get and Test Startup Ideas - Michael Seibel
- Start with ideas is tricky, start with a problem.
- Having a personal connection to a problem is helpful.
- Idea books -> Problem books.
- Why are you uniquely qualified to work on this problem?
- MVP (Minimal viable product)
- Don’t fall in love with your MVP. Be in love with your problem and customer. Treat your product in a way that it can change.
- Initial users
- Almost handpicked. Have the right type of initial users.
How to Get and Evaluate Startup Ideas | Startup School
- 10 questions to ask about any startup idea
- Do you have founder/market fit? (Pick a good idea for your team)
- How big the market? (Big now, or small but rapidly growing)
- How accute is the problem?
- Do you have competition? (Good ideas typically have some competitions)
- Do you want this?
- Did this only recently become possible/necessary? (New need. Example: background checker api when Uber took off)
- Are there good proxies for this business? (Someone succeed, but not your direct competitor)
- Is this an idea you’d want to work on for years?
- Is this a scalable business?
- Is this a good idea space? (Like Fintech, it has a good hit rate)
- 3 things that make your startup idea good
- Hard to get started (Stripe)
- Boring space (Payroll idea has more hit rate than apps to find a good restaurant / song to listen to)
- Existing competitors (Dropbox)
- How to come up with startup ideas (organically > thinking of ideas)
- Become an expert on something valuable.
- Work at a startup.
- Build things you find interesting.
- 7 recipes for generating startup ideas
- Start with your team is especially good at.
- Start with a problem you’ve personally encountered.
- Think of every job you’ve had (+ internships + life experiences)
- What are problems or opportunities you’ve been in a special position to see?
- Think of things you personally wish existed. (Dangerous)
- Look for things in the world that have changed recently.
- Look for new variants of successful companies.
- Talk to people and ask what problems they have.
- First picking a fertile idea space.
- Talk to potential customers, and also other founders.
- Look for big industries that seem broken.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.